How to Manage AI Risk while Supporting Innovation
Artificial intelligence is embedded in how businesses market, hire, analyse data, interact with customers, and make decisions. This can cause risks such as legal, ethical, operations and reputation risks.
Effective AI risk management is about structure. When done well, it actually enables faster, safer adoption.
Below is a summary of how to manage risks.
1. Understand the potential AI risks
AI risks can include:
2. Classify Your AI Use Cases
Not all risks should have the same controls to every AI system.
A chatbot that answers FAQs is very different from:
an AI tool screening job candidates
an algorithm determining pricing
an AI model analysing health, financial or behavioural data
Start by classifying AI systems based on:
Who is affected? (customers, employees, the public)
What decisions are influenced? (informational vs consequential)
What data is used? (personal, sensitive, proprietary)
How autonomous is the system? (human-in-the-loop vs fully automated)
Higher-risk systems need more oversight. Lower-risk systems shouldn’t be smothered with unnecessary red tape.
3. Build Governance before controls
When building a governance framework, businesses need to figure out:
Who owns this AI system?
Who is responsible if it goes wrong?
Who can approve changes?
Who monitors performance and risk?
An AI Governance Framework should define
Defined roles and accountability
Approval thresholds based on risk
Escalation pathways
Documentation standards
Without governance, controls won’t be effective.
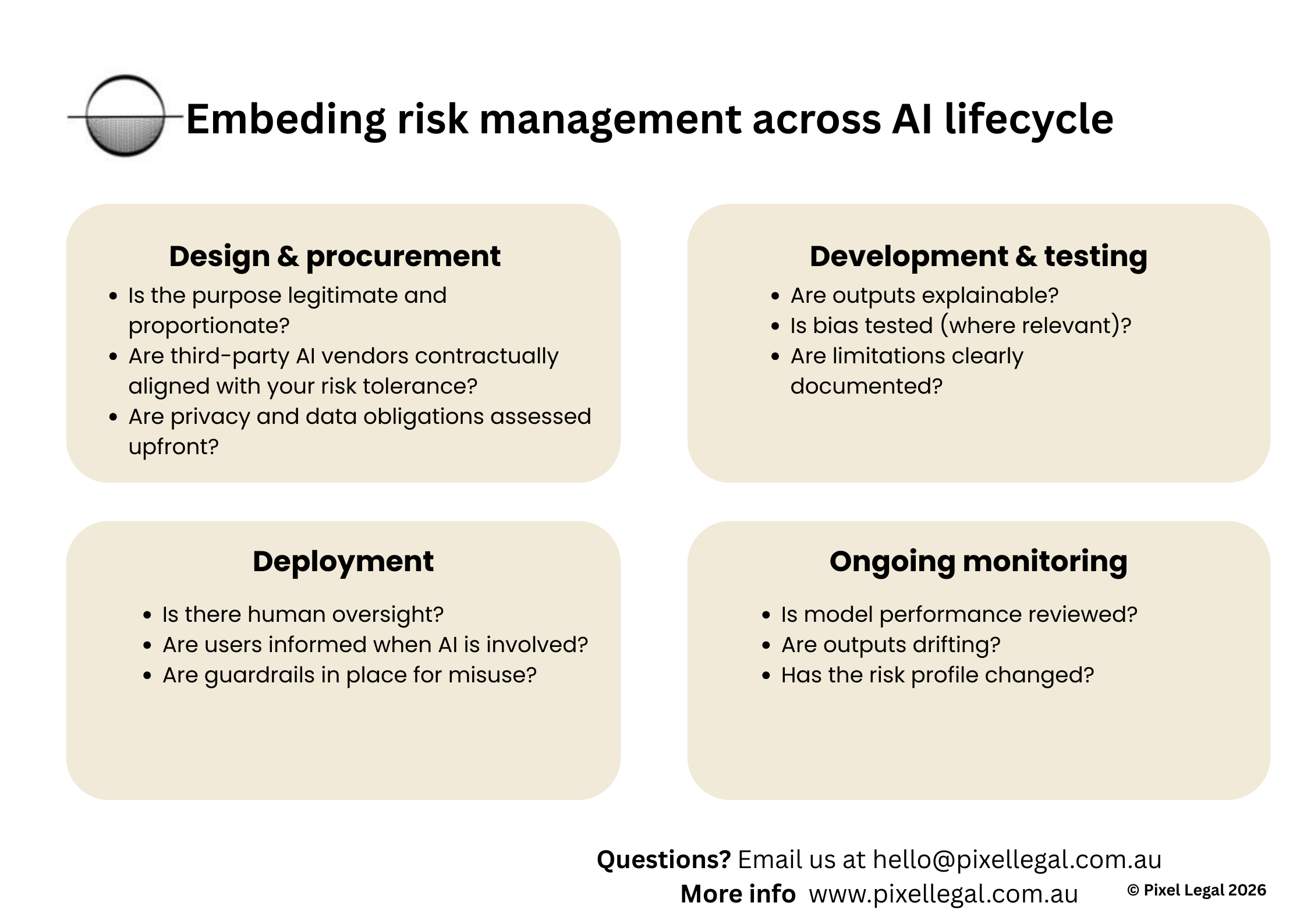
4. Embed Risk Management Across the AI Lifecycle
AI risk changes over time. What’s low-risk at design can become high-risk at deployment.
A practical approach is to think in stages:
5. Identify the legal issues /risks
Common issues include:
Terms that don’t address AI use or limitations
Privacy policies that don’t reflect AI processing
No internal AI use policy for staff
No contractual protections when using third-party AI tools
Strong foundations reduce risk before something goes wrong
6. Risk management
The objective is to:
understand it
document decisions
apply controls proportionate to impact
Businesses that do this well move faster — because decision-makers feel confident approving AI use rather than blocking it out of fear.
Summary
AI is transforming how businesses operate, but it introduces legal, data, operational, reputational, and governance risks. Effective AI risk management is not about avoiding AI — it is about creating structure so businesses can adopt AI confidently and safely.
This involves understanding potential risks, classifying AI tools based on impact, establishing clear governance and accountability, managing risk throughout the AI lifecycle, and ensuring legal documents and policies properly address AI use.
The goal is not to eliminate risk, but to understand and manage it proportionately. Businesses that take this structured approach are typically able to innovate faster because decision-makers have confidence in how AI is being used.
Any questions?
Reach out to hello@pixellegal.com.au or book an appointment